When it comes to photography, your choice of camera equipment can make a world of difference in the quality of your images. One of the most critical decisions you’ll face is selecting the right camera sensor, and that’s precisely what we’re here to help you within this comprehensive guide on APS-C vs. Full-Frame sensors.
Importance of Choosing the Right Camera Sensor
Imagine you’re an artist about to create a masterpiece on a canvas. The canvas’s size and texture significantly impact the final artwork’s details and visual appeal. In photography, the camera sensor is your canvas, and its size plays a similar role. It’s not just a technical aspect; it’s a creative one too.
The camera sensor is the heart of your camera, responsible for capturing the light and transforming it into digital images. Its size affects various aspects of your photos, such as image quality, low-light performance, depth of field, and more. Choosing the right sensor for your needs can be the difference between good and exceptional photographs.
Overview of APS-C and Full-Frame Sensors
Before diving deeper into the APS-C vs. Full-Frame sensor comparison, let’s get acquainted with these two sensor types.
- APS-C Sensor: APS-C, short for Advanced Photo System type-C, is a sensor size commonly found in many digital cameras, especially those designed for enthusiasts and professionals. It’s smaller than a Full-Frame sensor, typically measuring around 22mm x 15mm. APS-C sensors strike a balance between image quality and portability.
- Full-Frame Sensor: Full-Frame sensors, on the other hand, are larger, measuring approximately 36mm x 24mm. They are often found in high-end professional cameras and are known for delivering exceptional image quality, especially in low-light conditions.
Purpose of the Ultimate Guide
You might be wondering why we’ve created this ultimate guide on APS-C vs. Full-Frame sensors. Well, the world of photography is diverse, and no one-size-fits-all solution exists. We’ve crafted this guide to empower you with the knowledge needed to make an informed decision tailored to your unique photography journey.
Our aim is to make things easier for you by breaking down all the technical terms and giving you the knowledge you need to fully comprehend the differences between APS-C and Full-Frame sensors. By the time you finish reading this guide, you’ll have a better idea of which sensor type is perfect for your photography style, goals, and budget. So, let’s get started!
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the nuances of APS-C and Full-Frame sensors, exploring their advantages, limitations, and real-world applications. We’ll also provide you with valuable insights, tips, and real-life examples to help you make a choice that will elevate your photography game.
Understanding Camera Sensor Basics
1- What is a Camera Sensor?
A camera sensor is a type of image sensor that converts light into an electrical signal. It is the most important component of a digital camera, and it is largely responsible for the quality of images that the camera can produce.
The camera sensor is located in the camera body behind the shutter as shown in the diagram below for both DSLR and mirrorless camera designs:
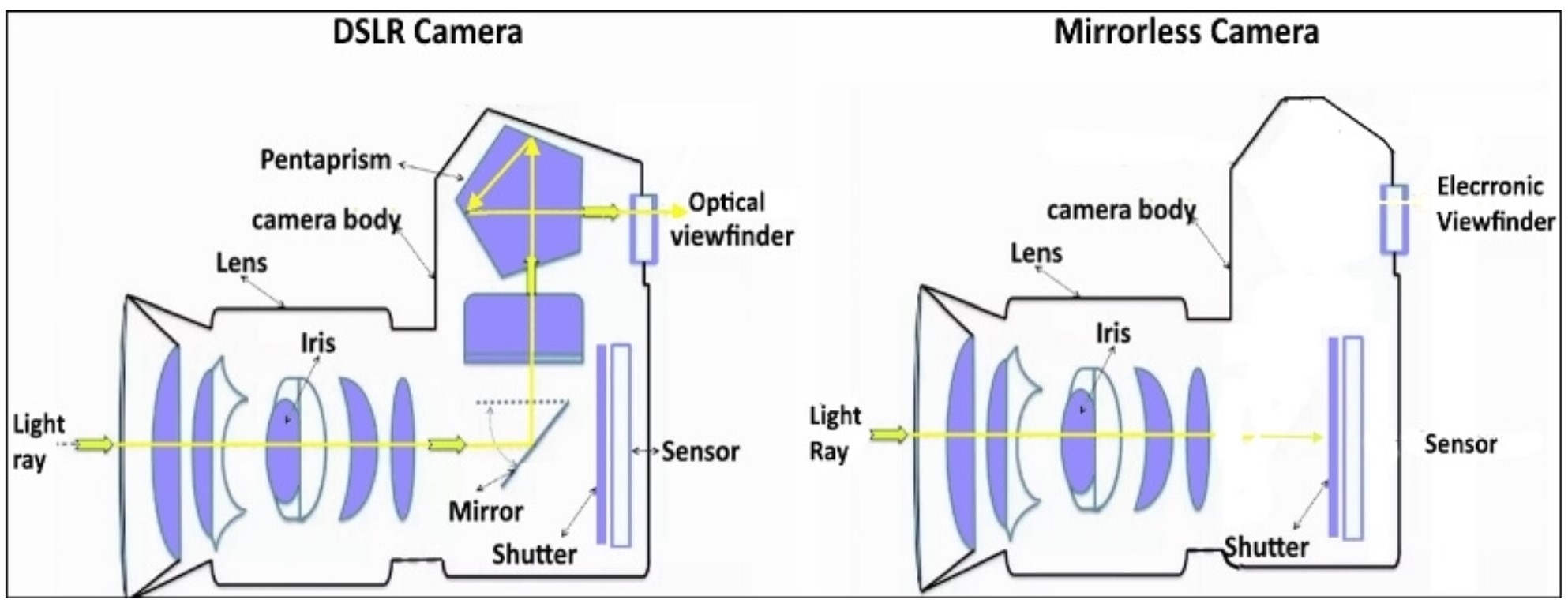
Camera sensors are made up of millions of tiny light-sensitive elements called photosites. When light strikes a photosite, it creates an electrical charge. The amount of charge created depends on the brightness of the light. The camera then converts these electrical charges into digital signals, which are used to create an image.
Photo by Depositphotos
There are two main types of camera sensors: charge-coupled devices (CCDs) and complementary metal-oxide-semiconductors (CMOS). CCD sensors are generally more expensive than CMOS sensors, but they offer better image quality in low-light conditions. CMOS sensors are more common in consumer cameras because they are cheaper to produce and consume less power.
Now, let’s dig deeper into how the sensor size affects the quality of those images.
2- How Sensor Size Affects Image Quality
One of the most critical factors to consider when comparing APS-C vs. Full-Frame sensors is their physical size. The sensor’s size plays a significant role in determining image quality, and here’s why:
-
Resolution:
Sensor size does not directly affect sensor resolution, but it does limit the maximum resolution that a sensor can achieve. The resolution of a camera sensor is measured in megapixels. A megapixel is one million pixels, and the higher the resolution, the more detail the sensor can capture.
Sensor resolution is determined by the number of pixels on the sensor. The more pixels on the sensor, the higher the resolution. However, there is a limit to how many pixels can be packed onto a sensor without sacrificing image quality.
This is because each pixel needs a certain amount of space to capture light effectively. If the pixels are too small, they will not be able to capture enough light, which will result in a noisy image. The larger the sensor, the more space there is for each pixel, which means that the sensor can have a higher resolution without sacrificing image quality.
-
Light Gathering Capacity:
Sensor size directly affects light-gathering capacity. A larger sensor has more surface area, which means it can capture more light. This is why larger sensor cameras perform better in low-light conditions.
For example, a full-frame camera sensor has a much larger surface area than a smartphone camera sensor. This means that a full-frame camera can capture much more light in the same amount of time, which results in better image quality in low-light conditions.
The amount of light that a sensor can gather also depends on the pixel size. Larger pixels can capture more light than smaller pixels. However, pixel size is not the only factor that affects light-gathering capacity. Sensor size is also important.
For example, a full-frame camera sensor with large pixels can capture much more light than a smartphone camera sensor with large pixels. This is because the full-frame camera sensor has a much larger surface area.
-
Depth of Field:
Sensor size affects depth of field in two ways:
- Directly: Larger sensors have a shallower depth of field than smaller sensors, all else being equal. This is because larger sensors require a longer focal length lens to achieve the same field of view as a smaller sensor. Longer focal length lenses have a shallower depth of field.
- Indirectly: Larger sensors often have larger pixels, which can also contribute to a shallower depth of field. This is because larger pixels can capture more light, which allows photographers to use wider apertures. Wider apertures have a shallower depth of field.
larger sensors will give you a shallower depth of field than smaller sensors. However, it is important to note that other factors such as focal length and aperture also play a role in depth of field.
-
Dynamic Range:
Sensor size affects dynamic range in a number of ways. First, larger sensors have larger photosites, which can capture more light. This means that larger sensors can record more detail in both the highlights and shadows of an image, resulting in a wider dynamic range.
Second, larger sensors are less susceptible to noise, which can also improve dynamic range. Noise is a grainy effect that can appear in images, especially in low-light conditions. Larger photosites are less susceptible to noise because they can capture more light, which helps to reduce the signal-to-noise ratio.
Third, larger sensors often have better image processing capabilities, which can also improve dynamic range. Image processing software can be used to reduce noise and improve contrast, which can both help to extend the dynamic range of an image.
APS-C Sensor Explained
Now that we’ve covered the basics of camera sensors and how sensor size impacts image quality, let’s take a closer look at APS-C sensors. Understanding what they are, their advantages, limitations, and common uses will give you valuable insights into why they’re a popular choice among photographers.
1- What is APS-C Sensor?
APS-C, which stands for Advanced Photo System type-C, is a type of image sensor used in many digital cameras, particularly those aimed at photography enthusiasts and professionals. It gets its name from the Advanced Photo System film format, even though there’s no physical film involved.
In simple terms, APS-C sensors are smaller than Full-Frame sensors, measuring roughly 22mm x 15mm on average. This means that APS-C sensors have a crop factor, which is a multiplier that is applied to the focal length of a lens to determine its effective focal length on an APS-C camera. For example, a 50mm lens on an APS-C camera will have an effective focal length of 80mm (50mm * 1.6x crop factor).
This smaller size has both advantages and limitations, making APS-C sensors a versatile choice for various photography scenarios.
2- Advantages of APS-C Sensors
-
Size and Weight:
One of the most noticeable advantages of APS-C sensors is the size and weight of cameras that use them. APS-C cameras tend to be more compact and lightweight compared to their Full-Frame counterparts. This makes them perfect for travel, street photography, and situations where portability is crucial.
-
Cost:
Cost can be a significant factor for photographers, especially those starting their journey. APS-C cameras are generally more budget-friendly than Full-Frame alternatives, both in terms of the camera body and compatible lenses. This affordability allows you to invest in other essential accessories or expand your lens collection without breaking the bank.
-
Increased depth of field:
APS-C sensors have a smaller field of view than full-frame sensors, which means that they have a naturally deeper depth of field. This can be beneficial for some photography genres where you want to keep both the foreground and background in focus.
-
Increase in focal length:
The increase in focal length is an advantage of using an APS-C sensor. This is because APS-C sensors have a crop factor, which is a multiplier that is applied to the focal length of a lens to determine its effective focal length on an APS-C camera.
The increase in focal length can prove advantageous, particularly in the context of Wildlife photography. The utilization of APS-C cameras can enable the capture of wildlife subjects at a closer range, without the need for an exorbitantly priced telephoto lens. For instance, a 100mm lens on an APS-C camera can yield an effective focal length of 160mm, which is adequate for capturing close-up shots of numerous wildlife subjects.
Similarly, in the realm of Sports photography, APS-C cameras can be employed to freeze the action. A 300mm lens on an APS-C camera can produce an effective focal length of 480mm, which is sufficient to arrest the motion of even the swiftest subjects.
3- Limitations of APS-C Sensors
-
Lower Light Performance:
While APS-C sensors are versatile, they do have limitations, particularly in low-light conditions. Their smaller size means they can’t capture as much light as Full-Frame sensors. As a result, APS-C cameras might exhibit more noise (graininess) in low-light photos compared to their larger counterparts.
-
Narrower depth of field:
Depth of field, the range of distances in an image that appears sharp and in focus, is another aspect where APS-C sensors differ from Full-Frame sensors. APS-C cameras have a deeper depth of field, making it slightly more challenging to achieve that dreamy background blur (bokeh) that’s often sought after in portrait photography.
-
More limited lens selection:
There are fewer lenses available for APS-C cameras than for full-frame cameras. This is because APS-C cameras are less popular than full-frame cameras, and lens manufacturers tend to prioritize full-frame lenses.
-
Lower resale value:
APS-C cameras typically have a lower resale value than full-frame cameras. This is because APS-C cameras are less popular and because they tend to become obsolete more quickly.
4- Common Uses for APS-C Cameras
APS-C cameras find their place in various photography scenarios, thanks to their versatility and advantages. Here are some common uses for APS-C cameras:
- Travel Photography: The compact size and weight of APS-C cameras make them ideal companions for travelers. You can capture stunning landscapes, cityscapes, and candid moments without the burden of carrying heavy gear.
- Street Photography: When you’re out capturing the essence of the streets, a smaller camera can be less obtrusive and more comfortable to handle. APS-C cameras are a popular choice among street photographers.
- Wildlife Photography: APS-C cameras with telephoto lenses are often preferred by wildlife photographers. The crop factor of APS-C sensors can effectively extend the reach of your telephoto lenses, allowing you to get closer to your subjects.
- Amateur and Enthusiast Photography: Many hobbyist photographers and enthusiasts find APS-C cameras to be an excellent compromise between image quality, affordability, and portability.
In conclusion, APS-C sensors offer a compelling choice for photographers who value portability, affordability, and versatility. Understanding their advantages and limitations is crucial when making a decision in the APS-C vs. Full-Frame sensor debate.
The following are some famous camera models that use APS-c sensors.
In the next section, we’ll explore Full-Frame sensors in detail, providing a well-rounded view to help you make an informed choice for your photography needs.
Full-Frame Sensor in Detail
1- What is a Full-Frame Sensor?
In the realm of photography, Full-Frame sensors hold a revered status. They are the go-to choice for many professional photographers due to their exceptional image quality and versatility. But what exactly is a Full-Frame sensor?
A Full-Frame sensor, often referred to as a 35mm sensor, gets its name from the film era when it matched the size of a 35mm film frame. Today, it measures approximately 36mm x 24mm, making it significantly larger than the APS-C sensors we discussed earlier. This larger size comes with several advantages and some trade-offs.
2- Advantages of Full-Frame Sensors
-
Image Quality:
When it comes to image quality, Full-Frame sensors shine. They can capture more detail, produce stunning color accuracy, and offer a broader dynamic range. If you’re pursuing photography where image quality is paramount, such as high-end portraits, landscapes, or commercial work, a Full-Frame sensor is often the top choice.
-
Better low-light performance:
Full-frame sensors are larger than APS-C sensors, which means that they have more surface area to capture light. This gives full-frame cameras a significant advantage in low-light conditions.
-
Shallower depth of field:
Full-frame sensors have a larger field of view than APS-C sensors, which means that they can produce a shallower depth of field. This is often desired for portrait photography and other genres where you want to keep the subject in focus and blur the background.
-
Greater dynamic range:
Full-frame sensors have a wider dynamic range than APS-C sensors, which means that they can capture more detail in both the highlights and shadows of an image. This is especially beneficial for landscape photography and other genres where you need to capture a wide range of tones in a single image.
-
More lens selection:
There are more lenses available for full-frame cameras than for APS-C cameras. This is because full-frame cameras are more popular than APS-C cameras, and lens manufacturers tend to prioritize full-frame lenses.
-
Higher resale value:
Full-frame cameras typically have a higher resale value than APS-C cameras. This is because full-frame cameras are more popular and because they tend to hold their value better.
3- Limitations of Full-Frame Sensors
-
Size and Weight:
One of the primary limitations of Full-Frame cameras is their size and weight. The larger sensor requires a more substantial camera body and lenses. This can make Full-Frame setups bulkier and less convenient for travel or casual photography.
-
Cost:
Quality comes at a price, and Full-Frame cameras and lenses are generally more expensive than their APS-C counterparts. This can be a significant consideration, especially for photographers on a budget.
-
Lens selection:
While there is a wide range of lenses available for full-frame cameras, some specialty lenses, such as ultra-wide and super-telephoto lenses, can be very expensive.
-
Depth of field:
The shallower depth of field that is often desired for portrait photography can also be a disadvantage for other genres of photography, such as landscape photography, where you want to keep both the foreground and background in focus.
4- Common Uses for Full-Frame Cameras
Full-frame cameras are favored by professional and serious amateur photographers for a variety of reasons. Here are some common scenarios where Full-Frame cameras shine:
- Portrait Photography: The ability to achieve a shallow depth of field (that beautiful background blur) and excellent image quality make Full-Frame cameras a top choice for portrait photographers.
- Landscape Photography: When capturing the grandeur of landscapes, you’ll appreciate the rich detail, dynamic range, and color accuracy of a Full-Frame sensor.
- Wedding and Event Photography: Low-light performance and exceptional image quality are invaluable in capturing precious moments during weddings and events.
- Commercial and Product Photography: Full-frame cameras are often used in professional studios for product and commercial photography, where image quality and detail are essential.
- Astrophotography: Photographing the night sky demands excellent low-light performance, making Full-Frame sensors a preferred choice for astrophotographers.
In conclusion, Full-Frame sensors are known for their superior image quality and low-light performance, making them a top choice for professionals and photography enthusiasts. However, their larger size and higher cost may not suit everyone’s needs and budget. The choice between APS-C and Full-Frame sensors ultimately depends on your specific photography style, goals, and constraints.
The following are some examples of camera models that use full-frame sensors.
In the next section, we’ll dive into a detailed comparison of APS-C vs. Full-Frame sensors to help you make an informed decision.
APS-C vs. Full-Frame Sensor Comparison Summary
To sum up the previous discussion, the below table shows a comparison between the APS-c and Full-frame sensors
| Characteristic | APS-C Sensor | Full-Frame Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor size | Smaller than full-frame | Same size as 35mm film |
| Crop factor | 1.6x (Canon) or 1.5x (Nikon) | 1x |
| Field of view | Narrower | Wider |
| Depth of field | Deeper | shallower |
| Low light performance | Lower | Higher |
| Dynamic range | Lower | Higher |
| Lens selection | More limited | Wider |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Size and weight | Smaller and lighter | Larger and heavier |
| Resale value | Lower | Higher |
Factors to Consider When Choosing
When choosing between APS-C and Full-Frame sensors for your camera, several important factors should guide your decision. These factors help ensure that your camera aligns with your photography goals, style, and budget. Here are the key factors to consider:
1- Image Quality:
APS-C: APS-C sensors provide good image quality with sufficient detail for most photography genres. However, they may not match the image quality and dynamic range offered by Full-Frame sensors.
Full-Frame: Full-Frame sensors excel in image quality, offering excellent color accuracy, greater dynamic range, and more detail. They are the preferred choice for high-end photography.
2- Low-Light Performance:
APS-C: APS-C cameras can handle low-light situations reasonably well, but they may exhibit more noise (graininess) in photos compared to Full-Frame cameras.
Full-Frame: Full-Frame sensors are renowned for their exceptional low-light performance, capturing clean and detailed images even in challenging lighting conditions.
3- Depth of Field and Bokeh:
APS-C: APS-C sensors have a deeper depth of field, making it slightly more challenging to achieve a pronounced background blur (bokeh). However, it’s still possible with the right lenses and techniques.
Full-Frame: Full-Frame sensors offer a shallower depth of field, making it easier to create beautiful, creamy bokeh in your photos, especially in portrait photography.
4- Size and Weight:
APS-C: APS-C cameras and lenses are generally more compact and lightweight, making them ideal for travel, street photography, and portability.
Full-Frame: Full-frame cameras and lenses tend to be bulkier and heavier, which may be less convenient for on-the-go photography.
5- Cost:
APS-C: APS-C cameras and lenses are more budget-friendly, making them an excellent choice for photographers with financial constraints.
Full-Frame: Full-frame cameras and lenses are typically more expensive, catering to professionals and enthusiasts who prioritize image quality.
6- Common Uses:
APS-C: APS-C cameras are versatile and suitable for various photography styles, including travel, street, wildlife, and amateur photography.
Full-Frame: Full-Frame cameras shine in portrait, landscape, event, commercial, and astrophotography due to their superior image quality and low-light capabilities.
7- Lens Compatibility:
Consider the availability and cost of lenses for your chosen sensor. Full-frame lenses are often more expensive, so factor this into your decision-making.
8- Photography Style and Goals:
Your preferred style of photography and long-term goals should heavily influence your choice. If you aspire to become a professional or have specific photographic aspirations, your sensor choice should align with those ambitions.
9- Budget Constraints:
Your budget plays a significant role in your decision. Consider not only the camera body cost but also the cost of compatible lenses and accessories.
10- Future Upgrades:
Think about your long-term plans. If you foresee upgrading to more advanced equipment in the future, consider how your choice of sensor might affect your upgrade path.
In summary, the decision between APS-C and Full-Frame sensors should be based on your unique photography needs, style, and budget. Carefully weigh these factors to ensure that your chosen camera and sensor combination aligns with your goals and allows you to capture the best possible images in the scenarios you love to photograph.
Conclusion
In the APS-C vs. Full-Frame Sensor comparison, we’ve explored the fundamental differences that can make or break your photography experience. APS-C sensors offer versatility and affordability, while Full-Frame sensors deliver top-tier image quality and low-light performance.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. It all boils down to your unique photography style, goals, and budget. Make an informed choice by weighing factors like image quality, low-light capability, and depth of field against considerations like size, weight, and cost.
The key is informed decision-making. Know what you want to achieve, understand your gear’s strengths and limitations, and invest wisely in equipment that empowers your photography journey.
Whether you opt for the nimbleness of APS-C or the excellence of Full-Frame, embrace your choice, and let it elevate your photography to new heights. After all, it’s not just about the sensor; it’s about the stories you capture and the moments you cherish.
Thanks for reading, I hope you enjoyed the article, if you have any questions just drop them below & I will be happy to answer you.
The featured photo by Johnny_px from Pixabay
If you enjoy the site, don’t forget to subscribe, we will only inform you when a new article is posted.











Your guide comparing APS-C and full-frame sensors is incredibly insightful. I appreciate how you break down the advantages of each, making it easier for beginners like myself to understand. Have you personally noticed a significant difference in image quality between the two? I’m curious about your experiences.
Additionally, your explanation of the depth of field differences is particularly helpful. It’s something I’ve been trying to grasp for a while now. Do you have any tips for someone looking to experiment with different sensor sizes to better understand their impact on photography? Your expertise would be greatly appreciated. Thank you for sharing this comprehensive guide!
I’m glad you found the guide helpful! Yes, I’ve noticed differences in image quality, especially in low light and fine detail, between APS-C and full-frame sensors. To experiment with sensor sizes, consider renting cameras with both types and compare the results in various shooting conditions. It can provide valuable hands-on experience and help you understand their impact better. Feel free to ask if you have more questions – happy experimenting!
hey amin hashem,
thx for the article! it was very informative and helped me understand the difference between APS-C and Full-Frame sensors. i’ve been considering upgrading my camera, and this guide really clarified the pros and cons of each sensor type.
i’ve mostly used APS-C cameras in the past, and they’ve served me well for travel and street photography. but after reading this, i’m tempted to explore the possibilities of a Full-Frame camera, especially for portrait and landscape photography.
thx again for the great info, amin hashem! 🙂
You’re very welcome! I’m thrilled to hear that the article helped you understand the differences between APS-C and Full-Frame sensors. Exploring a Full-Frame camera for portrait and landscape photography can open up exciting possibilities. If you decide to make the switch, I hope it takes your photography to new heights. Feel free to reach out if you have any more questions in the future.
Best of luck on your photography journey!